6.3 KiB
6.3 KiB
项目地址:https://gitea.suimu.site/lennon/recommend_system
项目中给出两个算法,一个是基于用户的协同过滤算法,一个是基于物品的协同过滤算法。
数据处理
原始数据集说明
用户与课程关联数据集, 行数说明
| 字段 | 名称 | 示例值 | 描述 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| views | 浏览记录 | 60% | 用户对课程浏览进度 | (0%,100%) |
| favorites | 收藏记录 | 0 | 用户是否收藏课程,1 为收藏 | enum(0,1) |
| likes | 点赞记录 | 1 | 用户是否点赞课程,1 为点赞 | enum(0,1) |
| comments | 评论记录 | ["Loved it", "Would buy again"] | 用户对课程的评论,为字符串数组 | ["Great product!", "Loved it", "Would buy again"] |
| shares | 分享记录 | 1 | 用户是否分享课程,1 为分享 | enum(0,1) |
| feedbacks | 反馈记录 | [ "Shipping was fast"] | 用户对课程的反馈,为字符串数组 | ["The product was good", "Shipping was fast"] |
| ratings | 评分记录 | 3 | 用户对课程的评分 | (1,5) |
中间状态,文本情感计算
处理文本情感之后的数据,示例如下:
| 用户编码 | 课程编码 | 浏览记录 | 收藏记录 | 点赞记录 | 评论记录 | 分享记录 | 反馈记录 | 评分记录 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.28 | 1 | 0 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.87 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 | 0.49 | 0 | 1 | 0.76 | 0 | 0.65 | 3 |
其中,评论记录和反馈记录通过 NLP 的情感分析,得到 (0,1)之间的两位小数。偏向 1 表示正向情感。
pip install snownlp
from snownlp import SnowNLP
text1 = "这个产品真的很好用!"
s = SnowNLP(text1)
print(s.sentiments) # 输出情感得分 0.8380894562907347
from snownlp import SnowNLP
text = "好烦啊,和参数对不上!"
s = SnowNLP(text)
print(s.sentiments) # 输出情感得分 0.2734196629160368
计算 User-Item 的评分
在原始 ml-100k 数据集中,用户和电影之间的评分是手动打的,本项目中的实现逻辑也比较简单。计算物品或者用户的邻居逻辑都在类 CoreMath中。所以这边需要根据 浏览记录、收藏记录、点赞记录、评论记录、反馈记录、评分记录等信息计算出一个评分。
实现逻辑是将所有的信息都标准化为一个 0 到 1 之间数,然后按照不同信息的重要程度给一个权重。计算出一个 1 到 5 之间的分数。这样就不需要改动原有算法的代码了。
权重分配说明:
- 浏览记录 (views): 虽然浏览行为重要,但它属于较为被动的行为。建议赋予较低的权重。
- 收藏记录 (favorites): 收藏表明用户对产品有一定的兴趣,建议赋予中等权重。
- 点赞记录 (likes): 点赞表示用户的积极反馈,建议赋予中等偏高的权重。
- 评论记录 (comments): 评论能直接反映用户的想法,建议赋予较高的权重。
- 分享记录 (shares): 分享表明用户愿意向他人推荐产品,建议赋予中等偏高的权重。
- 反馈记录 (feedbacks): 反馈通常比评论更详细,建议赋予较高的权重。
- 评分记录 (ratings): 评分是最直接的用户评分,建议赋予最高的权重。
权重分配建议
weights = {
'views': 0.05, # 浏览记录:较低权重
'favorites': 0.1, # 收藏记录:中等权重
'likes': 0.15, # 点赞记录:中等偏高权重
'comments': 0.2, # 评论记录:较高权重
'shares': 0.15, # 分享记录:中等偏高权重
'feedbacks': 0.2, # 反馈记录:较高权重
'ratings': 0.15 # 评分记录:最高权重
}
代码示例
from typing import Dict
from snownlp import SnowNLP
def calculate_composite_score(
views: float,
favorites: int,
likes: int,
comments: list[str],
shares: int,
feedbacks: list[str],
rating: int,
weights: Dict[str, float] = None
) -> float:
if weights is None:
print("No weights provided, using default values.")
weights = {
'views': 0.01,
'favorites': 0.1,
'likes': 0.125,
'comments': 0.175,
'shares': 0.125,
'feedbacks': 0.175,
'rating': 0.29
}
print(f"Weights: {weights}")
# 量化 comments 和 feedback 数据,如果列表为空则默认为0
avg_comment_score = np.mean([SnowNLP(comment).sentiments for comment in comments]) if comments else 0
avg_feedback_score = np.mean([SnowNLP(feedback).sentiments for feedback in feedbacks]) if feedbacks else 0
# 格式化为两位小数
avg_comment_score_formatted = round(avg_comment_score, 2)
avg_feedback_score_formatted = round(avg_feedback_score, 2)
print(f"Average comment score: {avg_comment_score_formatted}")
print(f"Average feedback length: {avg_feedback_score_formatted}")
# 将评分数据缩放到 0-1
scale_rating = rating * 0.2
# Calculate the weighted score
score = (
views * weights['views'] +
favorites * weights['favorites'] +
likes * weights['likes'] +
avg_comment_score_formatted * weights['comments'] +
shares * weights['shares'] +
avg_feedback_score_formatted * weights['feedbacks'] +
scale_rating * weights['rating']
)
print(f"Score: {score}")
# Ensure the score is in the range [1, 5]
score = max(1, min(5, score * 5))
return round(score, 2)
# 示例用法
views = 75 * 0.01 # 假设 75% 的用户浏览了这个 item
favorites = 1
likes = 0
comments = ["非常棒的产品!", "超爱的", "下次还买"]
shares = 1
feedbacks = ["产品很好", "发货速度很快"]
rating = 5
composite_score = calculate_composite_score(views, favorites, likes, comments, shares, feedbacks, rating)
print("Composite Score:", composite_score)
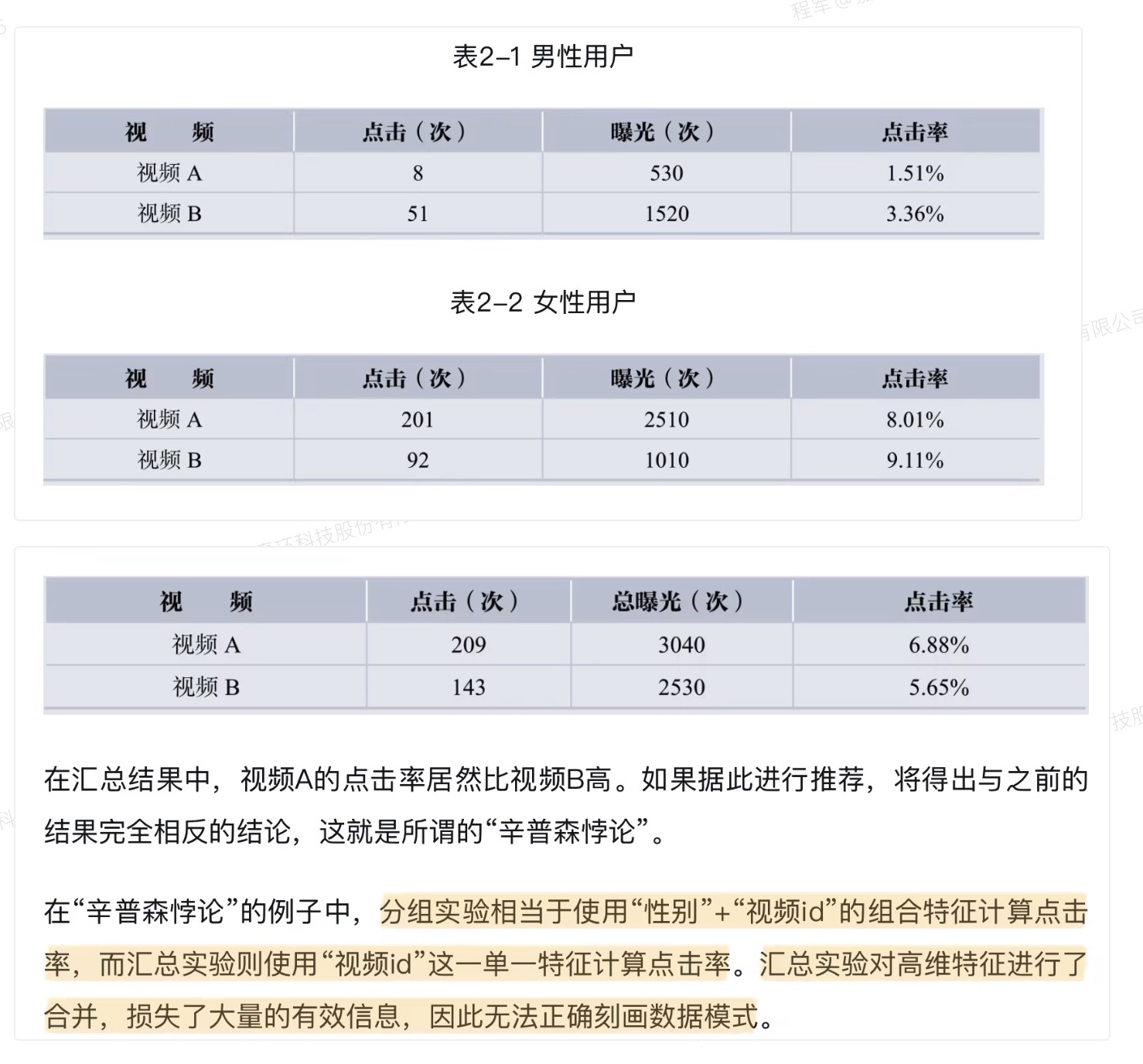
算法缺点
问题
这种融合的计算方式会导致辛普森悖论
改进方案
将 1-5 的分数值换成多维的评分向量,比如 [0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.1, 0.1],这样每个维度的权重可以不同, 当然计算时消耗的资源也会增加。